コンプリート! xy xy boolean algebra 237213-X'y+xy' boolean algebra
Boolean Expression Minimizer provides stepbystep simplification of Boolean algebra expressions Two modes are available 1 Interactive Algebraic Minimizer In this mode, you are guided to simplify an expression Hints are provided and expressions are tested for validity and equivalence in each step 2Neutral function Neutral function in which a number of minterms are equal to the number of max terms The number of neutral function possible are \(~^{2^n}C_{2^{n1}}\) For n variables, the total number of terms possible = number of combinations of n variables = 2 n;LAWS AND THEOREMS OF BOOLEAN ALGEBRA Identity Dual Operations with 0 and 1 1 X 0 = X (identity) 3 X 1 = 1 (null element) 2 X1 = X 4 X0 = 0 Idempotency theorem 5 X X = X 6 XX = X Complementarity 7 X X' = 1 D = X Y Z Back to EE0 Homepage

Logic Circuits Lecture 3 By Amr Al Awamry Basic Definitions Binary Operators And Z X Y X Yz 1 If X 1 And Y 1 Or Z X Y Z 1 If X 1 Or Y 1 Ppt Download
X'y+xy' boolean algebra
X'y+xy' boolean algebra-X AND y x y;C) (xy′z)(x′z′)(xy)′ = (xy′z)′(x′z′)′(xy)′= x′yz′ xz x′y′ 27) Given Boolean function F1 and F2 a) Show that the Boolean function E = F1F2 contains the sum of the minterms of F1 and F2 b) Show that the Boolean function G = F1F2 contains the sum of the minterms of F1 and F2 F1= ∑ mi and F2= ∑ mj a)




Complete And Independent Sets Of Axioms Of Boolean Algebra Semantic Scholar
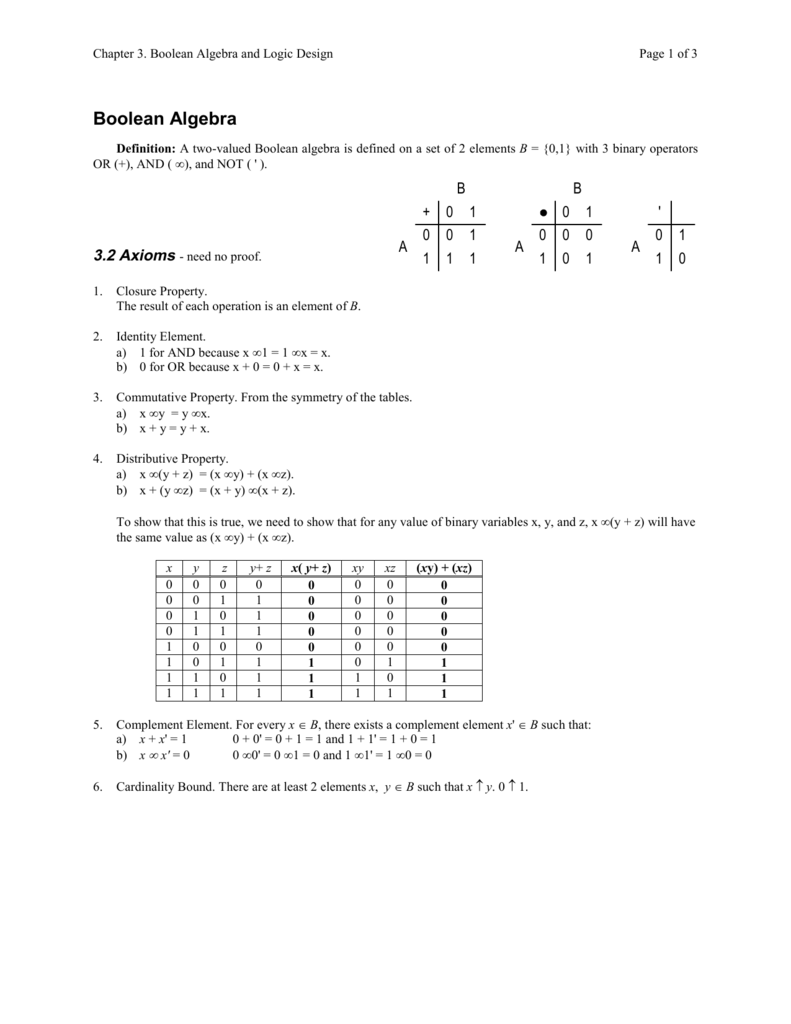
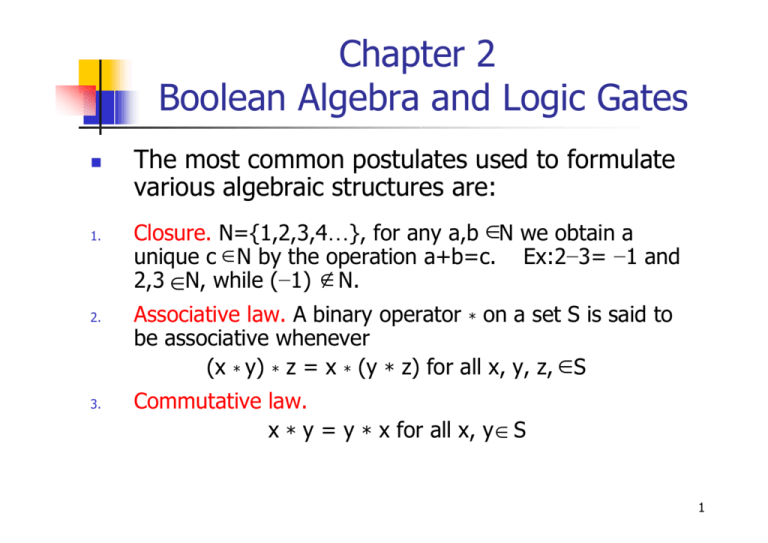
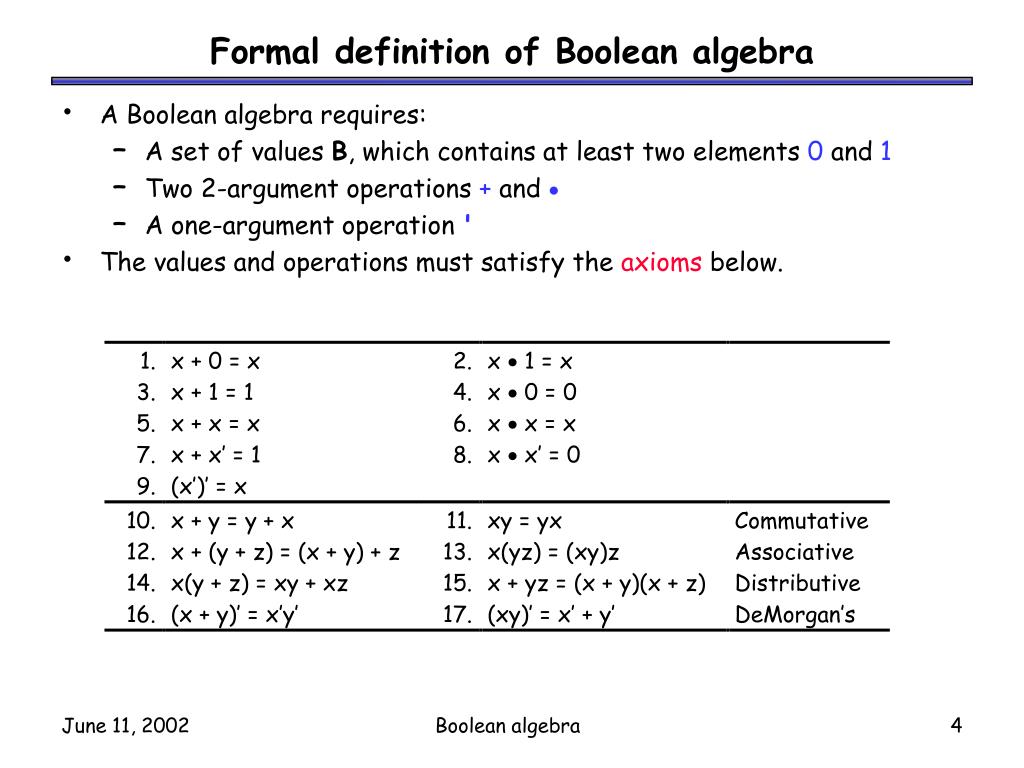
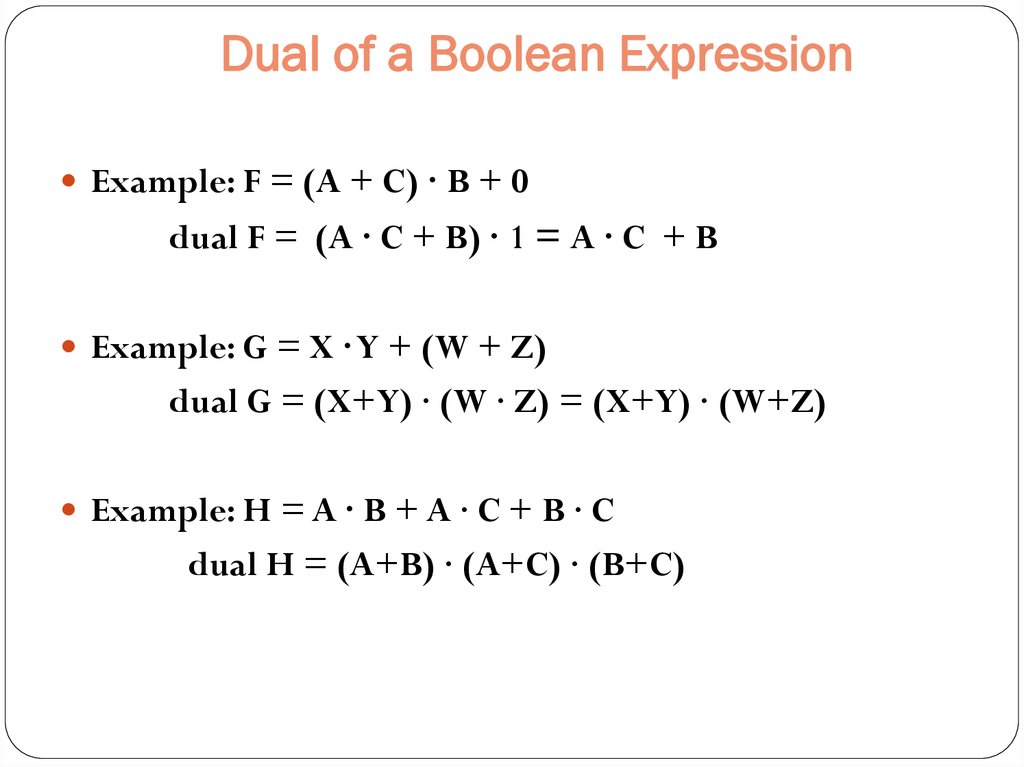
= xy x′(y′ yz) yz = xy x′y′ x′z yz = are equally valid functions and duality is a special property of Boolean (binary) algebra The property of duality exists in every stage of Boolean algebra For example, positive and negative logic schemes are dual schemes Similarly, AND is the dual of OR, NAND is the dual of NORNotation The following notation is used for Boolean algebra on this page, which is the electrical engineering notation False 0;5 Boolean Algebra • 1854 George Boole – Boolean Algebra • 1904 E V Huntington – Formal definition of Boolean Algebra • 1938 Claude E Shannon – Switching Algebra
Boolean Algebra and Digital Logic 31 Introduction 137 32 Boolean Algebra 138 321 Boolean Expressions 139 The OR operator is often referred to as a Boolean sum The expression xy is read "x or y" The truth table for OR is shown in Table 32 TABLE 32 The Truth Table OR Both x4 BOOLEAN ALGEBRA AND LOGIC SIMPLIFICATION BOOLEAN OPERATIONS AND EXPRESSIONS Variable, complement, and literal are terms used in Boolean algebra A variable is a symbol used to represent a logical quantity Any single variable can have a 1 or a 0 value The complement is the inverse of a variable and isX X' Y = X Y X (X' Y) = X Y Y X 0 1 0 1 Y X 0 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 X XY X' Y XX'Y X Y ECE 152A Digital Design Principles 14 Boolean Algebra The Consensus Theorem XY X'Z YZ = XY X'Z YZ X 00 01 0 1 11 10 1 1 1 1 XY X'Z YZ
Transcribed image text Simplify the following Boolean expressions using Boolean algebra only a xy žyz yz b (xy 2)(x y)z C xy z ( y)z 2) For theBoolean Algebra We all know that information in computers is represented as zeros (0) and ones (1), but how does the xyz xyz¯xyz¯ xy¯z¯ ¯xyz ¯x¯yz ¯x¯y¯z = x ¯y ¯z (m) Notice, that the rectangles must have dimensions that are a power of 2 1,2,4 Not 3When simplified with Boolean Algebra (x y)(x z) simplifies to (A) x (B) x x(y z) x(1 yz) (D) x yz Description Karnaugh map is used for the purpose of (A) Reducing the electronic circuits used (B) To map the given Boolean logic function To minimize the terms in a



Solved Simplify The Following Boolean Expressions To A Minimum Number Of Literals A Abc A B Abc B X Yz Xz C Xty X Ty D Course Hero




Q 2 2 Simplify The Following Boolean Expressions To A Minimum Number Of Literals A X Y Xy X Y Youtube
Four possible combinations x'y', x'y, xy', and xy> is called aminterm, or a standard product n variables can be combined to form minterms In a similar fashion, n variables forming an OR term provide possible combinations, calledmaxterms, or standard sums A Boolean functioncan be expressedalgebraically In the Boolean Algebra, verify using truth table that X XY = X for each X , Y in {0 , 1} asked in Computer by Helisha ( 6k points) basics of boolean algebraQ 218 For the Boolean functionF = xy'z x'y'z w'xy wx'y wxy(a) Obtain the truth table of F(b) Draw the logic diagram, using the original Boolean e



Boolean Algebra




Boolean Algebra Ece 152a Winter Pdf Free Download
X, Y are Boolean algebra variables Y XY • X 000 010 100 111 X Y X' Y' X • Y X' • Y' ( X • Y ) ( X' • Y' ) 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 ( X • Y ) ( X' • Y' ) ≡ X = Y X Y X' X' • Y 0010 0111 1000 1100 Boolean expression that is true when the variables X and YLaws and Theorems of Boolean Algebra Laws and Theorems of Boolean Algebra 1a X • 0 = 0 1b X 1 = 1 Annulment Law 2a X • 1 = X 2b X 0 = X Identity Law 3a X • X = X 3b X X = X (X Y) • (X Z) • (Y Z) = (X Y) • (X Z) Consensus Law 13b X Y X Z Y Z = X Y X Z Consensus Law 14a X ⊕ Y = (X YX y x' x'y xx'y xy 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 Stack Exchange Network Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers




Complete And Independent Sets Of Axioms Of Boolean Algebra Semantic Scholar




Boolean Algebra Laws
Chapter 3 Boolean Algebra and Logic Design Boolean functions can also be defined by a truth table Variable Values Function Values xy z F1F1'Stack Exchange network consists of 178 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow, the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers Visit Stack ExchangeThe precedence from high to low is AND, XOR, OR



Logic Design Logical Boolean Functions Steemit




The Boolean Expression X X Y Equals
6111 Spring 07 Problem Set 1 3 Problem 5 Setup and Hold Times for D FlipFlop (Flipflops will be covered in lecture 4) 1) Let a D latch be implemented using a mux and realized as follows You may assume the following a) G and G are complements and have zero skew, ie when G is 1, G is exactly 0, and vice versa xyz' xz = x(yz' z) = x(yz' z(y y')) = x(yz' yz y'z) = x(y(z z') y'z) = x(y y'z) = xy xy'z I used the fact that we can write any boolean variable A in the following way A = A(B B') = AB AB' as (B B') evaluates to 1 for any boolean variable B, so initial expression is not changed by ANDing it together with such an Boolean Algebra Laws and theorems cheat sheet The most important information you need to know before taking the Certified International Project Manager (CIPM) certification exam, by the International Association of Project Managers (IAPM)




Ch3 Boolean Algebra Cont D Pdf Free Download




Lecture 2 1 Boolean Algebra Inversion De Morgans
Terminology X X 0 1 1 0 3 • Recall Digital / Binary / Boolean 0 = False, 1 = True • Binary Variable a symbolic representation of a value that might be 0 or 1,Boolean Algebra Simplifying •Using the properties we can simplify Boolean expressions For example lets simplify the following expression F = x'y'z x'y z x y'It returns true if the value stored in x is less than the value stored in y The operands for relational operands are typically numeric (int or float), but we also use them to compare characters




Chapter 2 Basic Definitions B B Inary Operators A And Z X Y X Yz 1 If X 1 And Y 1 O Or Z X Yz 1 If X 1 Or Y 1 N Not Z




Introduction To Boolean Algebra Computer Architecture Tutorial Studytonight
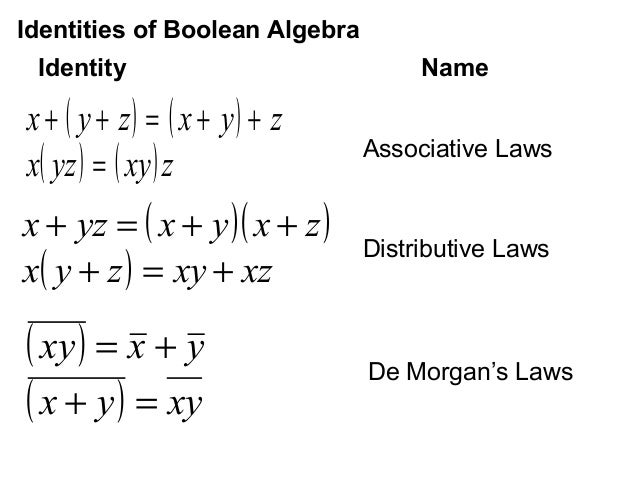
Just as is done is algebra Notice that Boolean addition defined here on {0,1} is NOT the same as the addition on the set of integers modulo 2 14 Example 141 Example 141 The following functions are equivalent (1) F(x,y) = xy (2) G(x,y) = xy xy xy Proof We show the two functions have the same values for every possible orderedSince a maximum number of terms possible = 2 n, so we choose half of the terms ie 2 n / 2 = 2 n1Distributive laws of Boolean algebra state that (i) X(Y Z) = XY XZ (ii) X YZ = (X Y)(X Z) 1 stlaw X(Y Z) = XY XZ holds good for all values of X, Y and Z in ordinary algebra whereas X YZ = (X Y)(X Z) holds good only for two values (0, 1) of X, Y and Z 14 Express in the Product of Sums form, the Boolean function F(x, y



Morris Mano Edition 3 Exercise 2 Question 2 Page No 69 Gate Overflow




Boolean Algebra Boolean Expressions And The Digital Circuits De Part 5
Q 22 Simplify the following Boolean expressions to a minimum number of literals (a) x'y'xyx'y (b) (x y)(x y') (c) x'yxy'xyx'y' (d) x'xyxz'xy'Boolean Algebra expression simplifier & solver Detailed steps, Logic circuits, KMap, Truth table, & Quizes All in one boolean expression calculator Online tool Learn boolean algebraAnswer (1 of 6) It took a moment for me to understand the notations I guess it's been longer than I thought, so let's review the notation * Multiplication represents AND Suppose FALSE is represented by zero (0) and TRUE is represented by one




Laws Of Boolean Algebra




Class 11 Computer Science Boolean Logic Soaring High
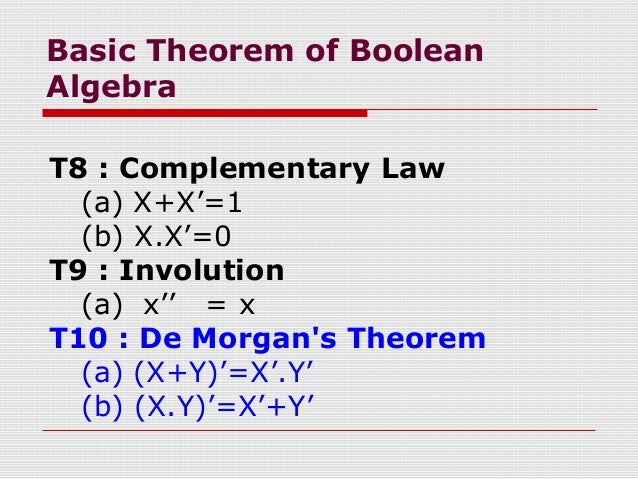
28 27 / 28 Homework 215 Given the Boolean function F = xy'z x'y'z w'xy wx'y wxy (a) Obtain the truth table of the function (b) Draw the logic diagram using the original Boolean expression (c) Simplify the function to a minimum number of literals using Boolean algebra (d) Obtain the truth table of the function from theX/y is not a Boolean expression xy is not a Boolean expression Definition Let B be a Boolean Algebra A Boolean function of n variables is a function f Bn B where f(x1,x2,,xn) is a Boolean expression in x1,x2,,xn Examples f(x,y,z)=xyx'z is a 3variable Boolean function The function g(x,y,z,w)=(xyz')(x'y'w)xyw' isStart by taking complement (') on both sides and use De Morgan's Laws to simplify both LHS and RHS to show they are equal De Morgan's Laws are (XY)' = X'Y' (XY)' = X' Y' This can be extended for more than 2 boolean variables For 3 variables it becomes (XYZ)' = X'Y'Z'



How To Use Boolean Algebra To Prove X X Y X Quora




Answered 6 A Prove With Boolean Algebra That Bartleby
The expression x < y is a boolean expression;12 One variable NOT AND OR XOR 13 XOR XOR can be defined in terms of AND, OR, NOT 14 Various Commutativity Associativity Distributivity ANDThe Boolean expression XX' Y equals XY Boolean algebra is the mathematics we use to analyze digital gates and circuits Use of "Laws of Boolean" to both reduce and simplify a complex Boolean expression in an attempt to reduce the number of logic gates required



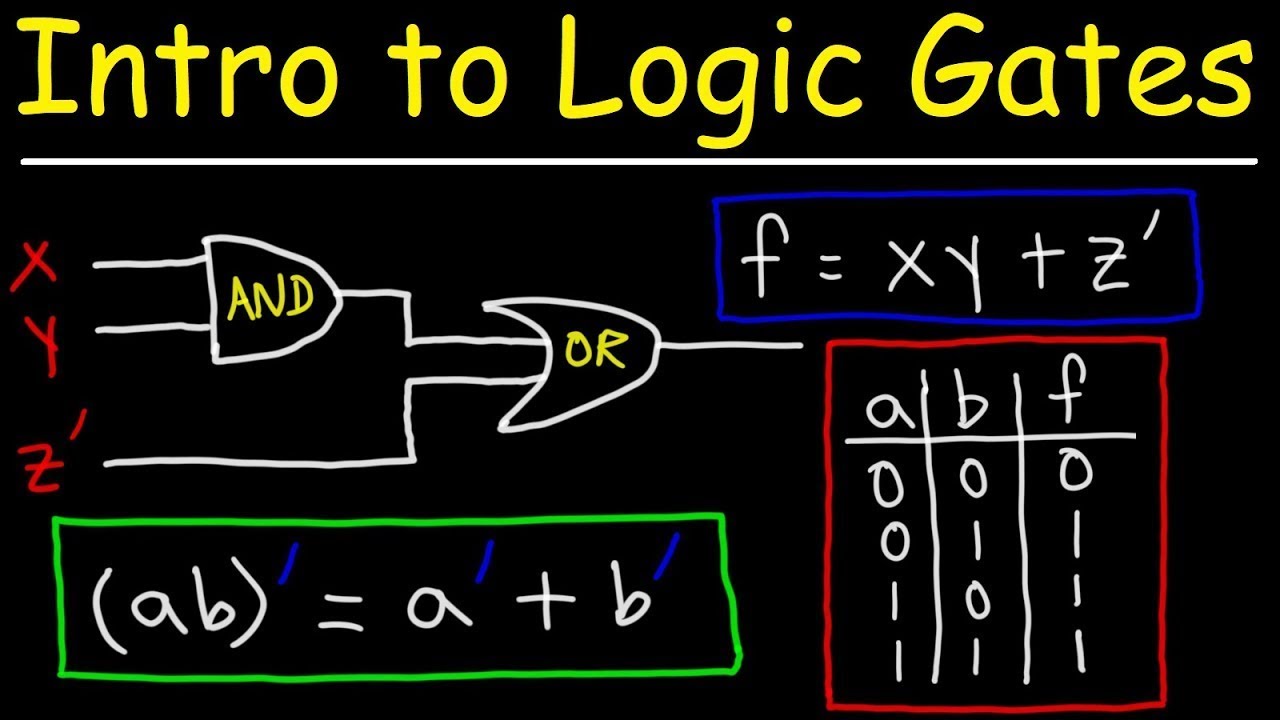
Logic Gates



2
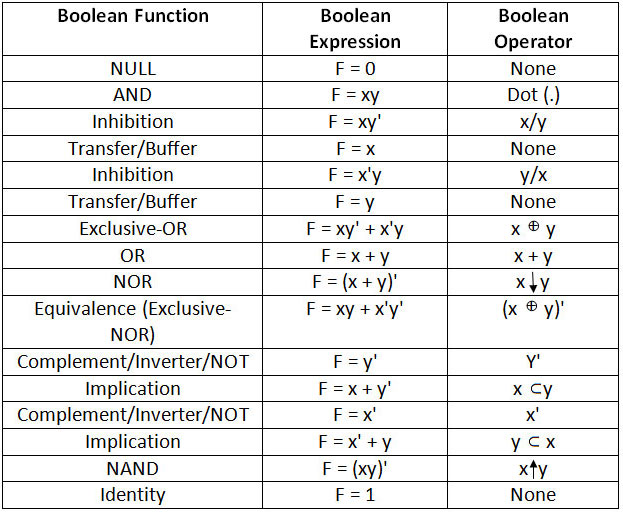
X OR y x y;Contents1 NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science – Boolean Algebra11 TOPIC1 Basics of Boolean Algebra12 TOPIC2 Karnaugh Map Minimization and Applications of Boolean Algebra NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Computer Science – Boolean Algebra TOPIC1 Basics of Boolean Algebra Very Short Answer Type Questions 1 mark each Question 1 Which gatesX XOR y x ⊕ y;




Boolean Algebra How To W 15 Step By Step Examples



Showch03
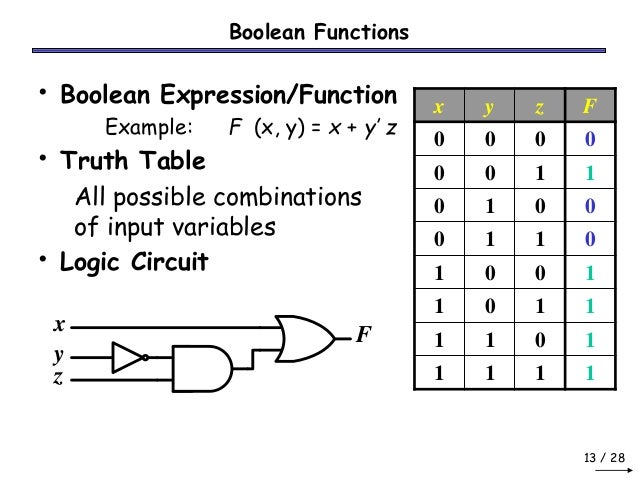
The most widely used theorems to solve the Boolean algebra are De Morgan's Laws These are of two types De Morgan's First Law and De Morgan's Second Law First law of De Morgan (x y)' = x' y' It states that the sum of their individual complement of a variable is equal to the complement of product of variableBoolean Algebra and Logic Gates cs309 G W Cox – Spring 10 The University Of Alabama in Hunt sville Computer Science Boolean Algebra The algebraic system usually used to work with binary logic expressions sville Computer Science Implementing a Boolean expression as a 12 Boolean Functions • A Boolean function is a function whose arguments, as well as the function itself, assume values from a twoelement set ({0, 1)}) • Example F(x, y) = x'y' xyz x'y • After finding the circuit inputs and outputs, you can come up with either an expression or a truth table to describe what the circuit does




06 Proof The Following Absorption Theorem Using The Fundamental Of Boolean Algebra X Xy X 07 Homeworklib




Solved I Have To Solve Boolean Expression By Complete Sum Of Products And Ia M Stuck Below Is What I Have Got E X Y Z X Ya Z Y Za E X Y Z X Ya Z Y Za Xy Xza Ya Zza E Xy Z Za X Y Ya Za Ya X Xa Zza E Xyz Xyza Xyza Xya Za Ya
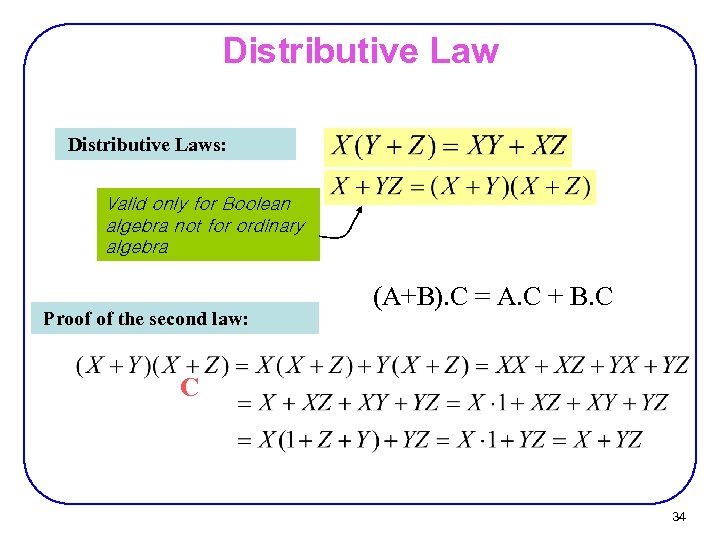
Boole's Intuition Behind Boolean Logic Variables X, Y, represent classes of things No imprecision A thing either is or is not in a class If X is "sheep" and Y is "white things," XY are all white sheep, XY = YX and XX = X If X is "men" and Y is "women," XY is "both men and women," XY = Y X and XX = X If X is "men," YTranscribed image text Huntington's Postulates • All properties of Boolean algebra can be proved from these properties xy = yX x (y z) = (x y) (x 2) x1 = x x y = y x x (y z) = (x y) (x 2) X0=X xx=0 xx=1 • We call these properties from which we derive the others axioms or postulates • Huntington's postulates are satisfied by the basic operators we have defined– Twovalued Boolean algebra is developed in a formal mathematical manner – This formalism is necessary to develop theorems and properties of Boolean algebra 11 Duality Principle • An important principle – x(x'y) = xy and xx' y = (xx')(xy) = xy




Pdf Cse3 Boolean Logic Practice Problems Solutions Jocet Quilaton Academia Edu




Boolean Logic
$=x(yy'z)x(y'z)$ But I don't know where to go from this step, I'm not sure if I'm allowe to rewrite y'z as yz' (I'm not even sure if that would help) booleanalgebra




Example Question Consider The Expressions A F Xy Xy Ppt Download



Boolean



All Boolean Logical Operations De Part 6
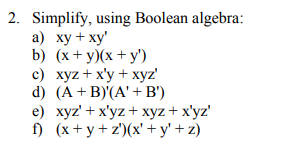



Solved 2 Simplify Using Boolean Algebra A Xy Xy B X Chegg Com




Boolean Algebra Gates And Digital Logic Boolean Algebra




Did I Simplify The Boolean Expression Correctly Mathematics Stack Exchange




Answered Simplify The Following Functional Bartleby




Ppt Question Consider The Expressions A F Xy Xy B B Xyz Xyz X Y Z X Y Z Powerpoint Presentation Id




In The Boolean Algebra Verify Using Truth Table That X Xy X For Each X Y In 0 1 Brainly In




Solved Simplify Following Using Boolean Algebra F X Yz X Y Xyz Xyz 6 Points Q Essaytaste



2




Q 3 3 Simplify Following Boolean Expressions Using Three Variable Maps A Xy X Y Z X Yz Youtube



2



Boolean Algebra How To W 15 Step By Step Examples




Boolean Algebra Simplification Question Proof Of Equation Mathematics Stack Exchange




2nd Puc Computer Science Question Bank Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra Kseeb Solutions




2nd Puc Computer Science Question Bank Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra Kseeb Solutions
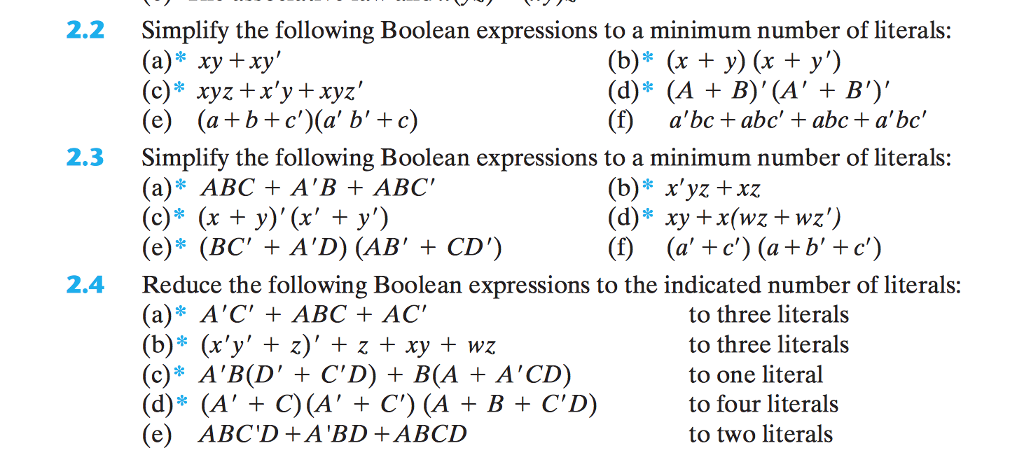



Solved 2 2 Simplify The Following Boolean Expressions To A Chegg Com




Boolean Algebra And Logic Gates 1 Boolean Algebra
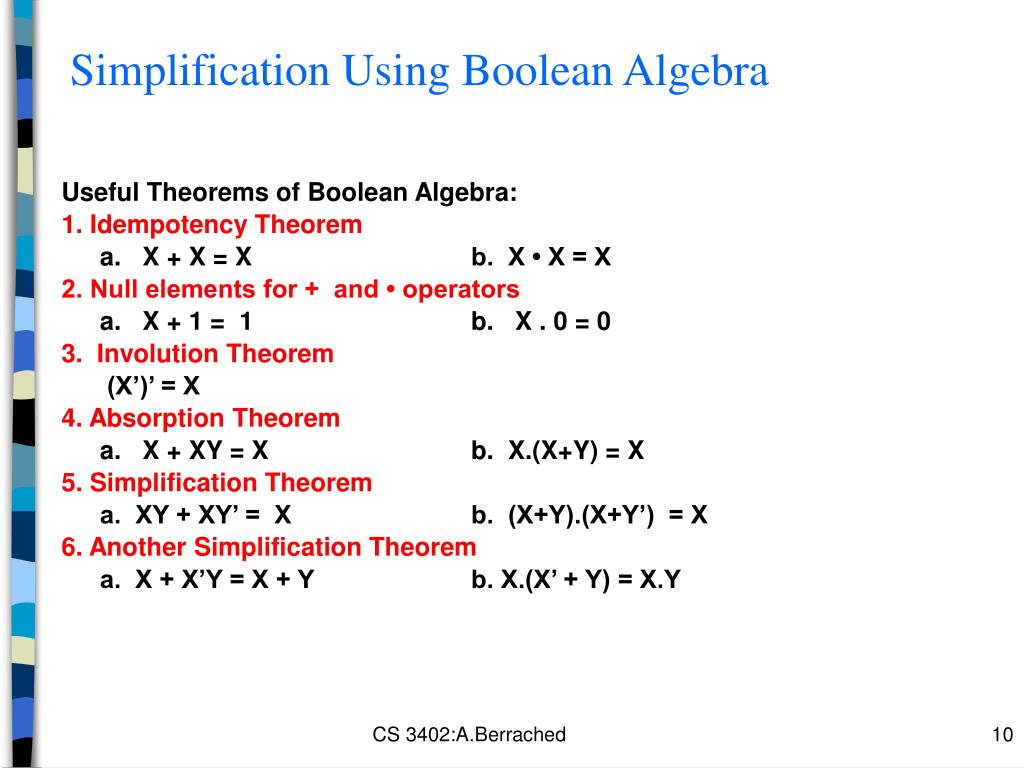



Ppt Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra And Logic Functions Powerpoint Presentation Id




Hasse Diagram Of The X Y Boolean Algebra Download Scientific Diagram




Nta Ugc Net Set Exams When Simplified With Boolean Algebra X Y X Z Simplifies To In Hindi Offered By Unacademy



1



How To Solve Boolean Algebra X Xy Xz Xy Z Quora



Showch03



2




Discrete Mathematics Boolean Algebra And Logic Circuits Duality



Chapter2 Boolean Algebra And Logic Gates
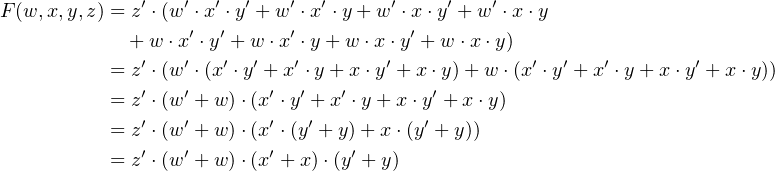



4 Logic Gates



Logic Gates Truth Tables Boolean Algebra And Or Not Nand Nor Youtube



Showch03



Homework 2 With Strategies Homework Eecs 31 Cse 31 Ics 151 Daniel D Gajski S Web Site



Boolean Algebra




Dpsd Notes Notes




Given The Boolean Function Fx Y Z 0 2 4 5 6 Reduce It Using Karnaughs Knowledgeboat




Logic Circuits Lecture 3 By Amr Al Awamry Basic Definitions Binary Operators And Z X Y X Yz 1 If X 1 And Y 1 Or Z X Y Z 1 If X 1 Or Y 1 Ppt Download




Boolean Algebra And Logical Functions Out4mind




Boolean Logic



ﺟﺒﺮ ﺑﻮﻝ Boolean Algebra ﺟﺒﺮ



2



How Could I Simplify This Boolean Expression X Y Y Z W X Z Quora




Boolean Algebra Computer Logic Design I Cecs 1 Docsity



1



Boolean Algebra




Pdf A Fast Computerized Method For Automatic Simplification Of Boolean Functions




Seven Segment Display Boolean Equations Example 2
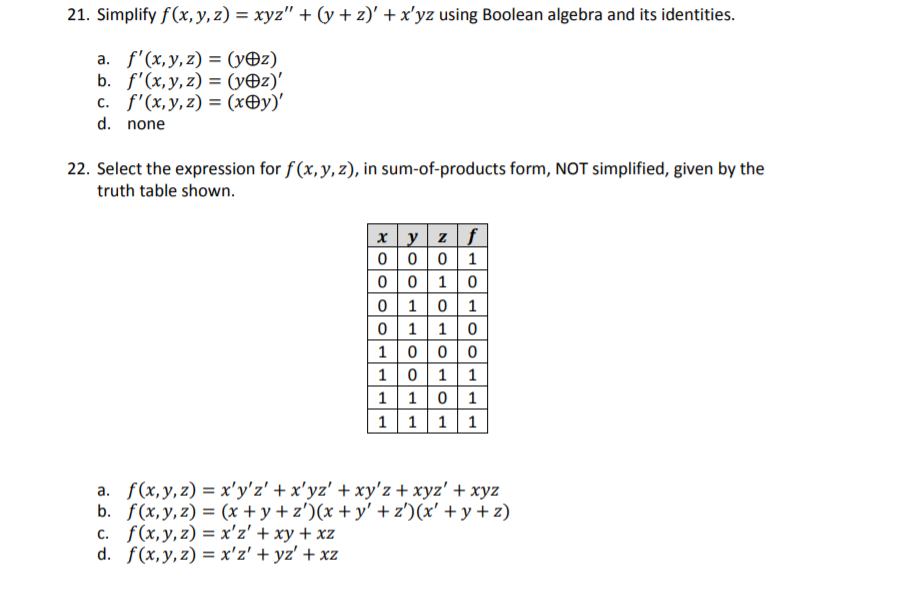



Solved 21 Simplify F Xyz Xyz Y Z X Yz Using Boolean Algeb




Boolean Algebra Boolean Expressions And The Digital Circuits De Part 5




Solved 1 Simplify The Following Expressions Using Boolean Chegg Com




Chapter 2 Boolean Algebra And Logic Gates Chapter



Ppt Boolean Algebra Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




21 Intro To Combinational Logic



Binary Variables Prezentaciya Onlajn



2




Lecture 4 Topics Boolean Algebra Huntingtons Postulates Truth



Dl Minimize Boolean Functions Gate Overflow




Solved Question 1 Which Of The Following Boolean Expression Chegg Com




Digital Electronics Boolean Algebra And Logic Gates Powerpoint Slides
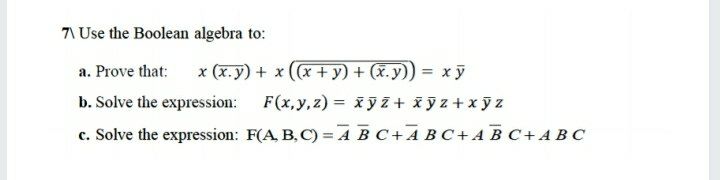



Answered Ause The Boolean Algebra To X X Y Bartleby




Digital Electronics Boolean Algebra And Logic Gates Powerpoint Slides
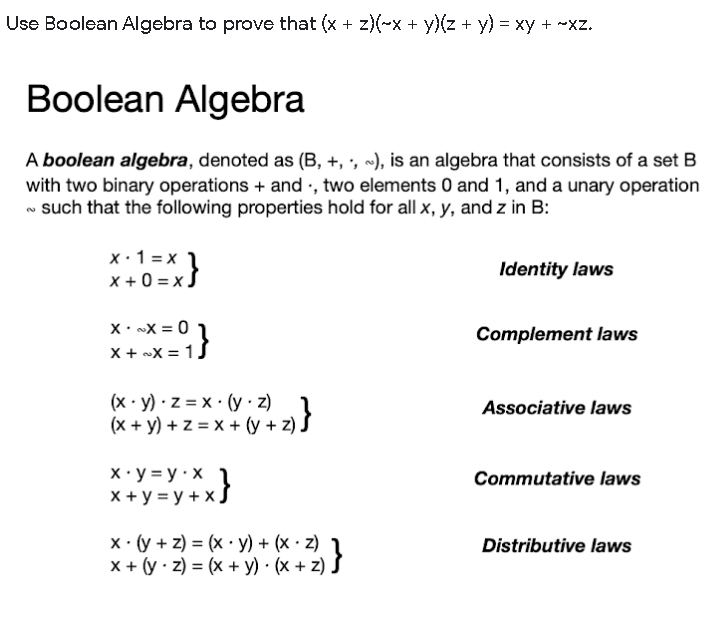



Solved Use Boolean Algebra To Prove That X Z X Y Z Chegg Com




Boolean Algebra Minimization Electrical Engineering Stack Exchange



2



2



In The Boolean Algebra Verify Using Truth Table That X Xy X For Each X Y In 0 1 Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



2




Boolean Algebras And Circuits Springerlink



Boolean Algebra Worksheet Digital Circuits




Boolean Algebra



2




Give Truth Table For The Boolean Expression X Y Brainly In




Problems Introduction To Digital Systems Modeling Synthesis And Simulation Using Vhdl Book




Boolean Algebra Show That Lhs Rhs Mathematics Stack Exchange




Circuits And Boolean Functions Sfdv05 Digital Logic




Chapter 1 Unit 2 Basic Postulates And Theorem Of Boolean Algebra Solutions For Class 12 Isc Apc Understanding Computer Science With Java Programs In Bluej Knowledgeboat




Boolean Algebra Ppt Download



Can Anyone Solve This Boolean Expression Prove That X Y Xyz Y Xz Y Y 1 Quora
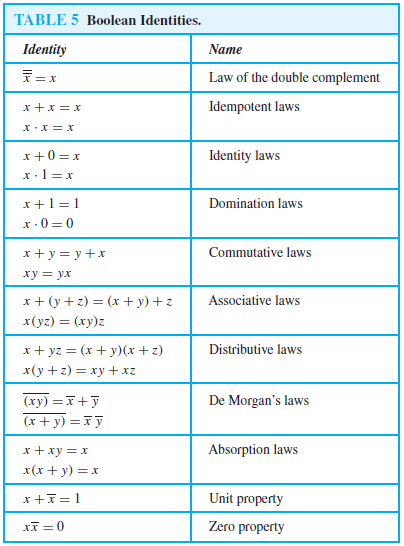



Identities Of Boolean Algebra
コメント
コメントを投稿